This Good Practice Guide is intended to promote a better understanding of power system harmonics within the industrial and commercial sectors. For more information or technical detail, please submit an enquiry below and one of our engineer consultants will happily provide more detail.
Power system harmonics can often seem to be a difficult and frustrating topic. A quick search for ‘harmonics’ will return an abundance of information that can be confusing and quite often misleading. A basic understanding of harmonic distortion, its cause and effects, and the various mitigating solutions that are nowadays available can benefit the modern site engineer, facility manager or maintenance technician.
What are Harmonics?
Modern power-electronic converters such as rectifiers, variable speed drives, soft-starters, inverters, UPSs and switch-mode power supplies are typical examples of non-linear loads. These ubiquitous devices utilise semiconductor switching technology to accurately control various parameters such as power output, speed, torque and electrical energy efficiency. They operate quite differently to linear loads (resistors, inductors, capacitors) that draw continuous current from the electricity supply. Instead, non-linear loads can draw short, rapid bursts of current from the supply, ie:
- Apply a sinusoidal voltage to a linear device and the current that flows will be sinusoidal.
- Apply a sinusoidal voltage to a non-linear device and the output will be non-sinusoidal.
The resultant non-sinusoidal waveform, (distorted by harmonics), can be broken down into various components that comprise a fundamental waveform of the same shape and frequency as the applied voltage plus multiple integers of this fundamental known as the harmonic components.
Different factors contribute to the level and severity of harmonic distortion to the supply voltage of an electrical system. Examples of these factors include the amount and type of non-linear load installed, amplitude and frequency of harmonic currents generated, and strength of supply (fault level) or system impedance of the electrical network in question.
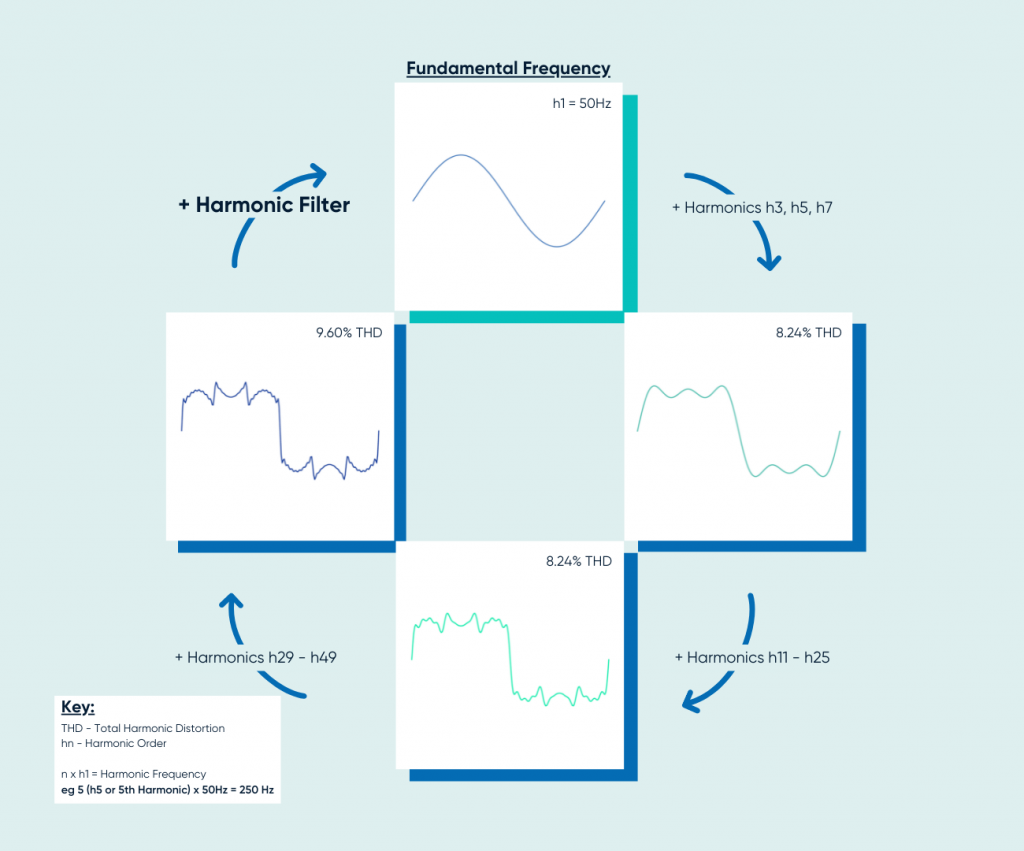
Differing levels of harmonic distortion
What are the Effects of Harmonics?
The detrimental effects of harmonic distortion manifest in many ways. Increased heating effects can lead to insulation breakdown and even premature failure of expensive site equipment such as distribution transformers, switchgear and associated conductors.
Capacitor banks typically used for power factor correction or voltage control are particularly susceptible to damage by harmonics due to their inherently low impedance at increased harmonic frequencies. (Caution should always be applied when installing capacitor banks to an electrical system to avoid system resonances at critical frequencies and amplification of harmonics).
Nuisance tripping of protective devices or fuse operations, mistimings of sensitive electronic equipment and interference of IT and telecommunications equipment are all possible unwanted effects of harmonic distortion. Increased maintenance and production downtime can run into high costs that affect a business’ bottom line.
Harmonic Surveys
If harmonics are suspected to be a possible cause of power quality issues at a given facility, then only a harmonic survey will prove the notion or otherwise. Although a growing concern with the ever-increasing use of semiconductors, don’t automatically assume that harmonics are the cause of all power quality phenomena – there can be many other possible causes. The trick is to identify or rule out harmonics as the cause. A professional harmonic survey is an investment that provides rapid payback and helps recommend the most appropriate solution or equipment and if the equipment is needed at all.
Harmonic analysers should be calibrated and traceable to ensure accurate readings and should be connected to the electrical incomer by a qualified engineer, adhering to the relevant health and safety standards. Method statements and risk assessments should always be provided when working with live electricity. Analysis of the harmonic measurements should be conducted by a qualified and experienced power systems engineer as it is the electrical network as a whole that needs to be studied. Current and voltage harmonic measurements can mean very little in isolation; rather it is their interaction with the electrical network in question that matters. Strength of supply or network impedance plays an important part in the study of harmonics and other connected equipment such as capacitor banks that can impact upon system resonant frequencies should also be investigated.
The written harmonic survey report should be understandable, with a clearly stated conclusion that defines if further action and corrective measures are needed.
This is where the professional harmonic survey pays for itself. If the level of harmonic distortion is not detrimental to your system, an unbiased professional report will tell you so. Potentially, a harmonic issue can be eliminated as the possible cause of your power quality issues and the need to install harmonic mitigating equipment ruled out.
On the other hand, if your harmonic survey identifies excess harmonics as the root cause of your power quality problems, then the information and recommendations contained within the report will enable the necessary engineering design to provide the most cost-effective solution. For added peace of mind to ensure that you are receiving sound engineering recommendations, make sure that your provider has professional indemnity insurance.
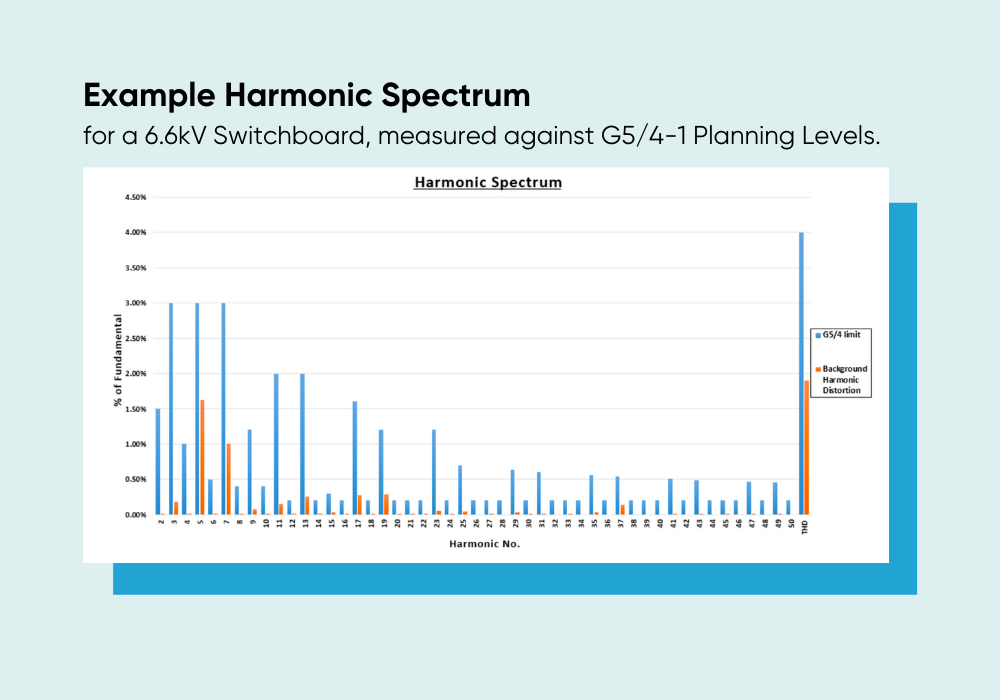
An example Harmonic Spectrum, showing total harmonic distortion and voltage distortion are compliant with G5/4-1 Planning Limits.
Harmonic Filtering Technologies
Passive, active, hybrid – which one do I need? There are various harmonic filter technologies available. Only careful consideration and diligent engineering analysis will provide the best possible engineered solution to an individual’s needs. Be sure that you are dealing with a company that can offer each of the various technologies to avoid the misrepresentation of one technology over the other and make sure that you are aware of the pros and cons of each of the possible options. For more information on harmonic filters and different harmonic filter types, click here.
If you have a specific question regarding harmonic filters and possible requirements, submit an enquiry below.